Both Docker and Node.js have risen in popularity in the past 5 years. Running Node.js on docker containers with docker-compose for local development is a great experience. In this step-by-step tutorial, we will look at how Node.js docker and docker-compose with multi-stage docker build work in sync. Time to get cracking!

Table of contents #
- Docker the new norm
- Node.js on Docker with high scalability
- Assumptions for Docker with Node.js
- Steps
- TLDR; Give me a quick run down
- Considerations
- Conclusion
Docker the new norm #
Docker has changed the way we software engineers work in the past 5-7 years.
Containers have made it easier to ship the whole stack including the OS, not just the code.
There is more than one reason to use docker everywhere, especially in the development environment. Docker was the second most loved platform in the Stack Overflow Survey 2020 same as 2019. The same survey 2020 edition also quotes
“We also see some year over year growth in the popularity of container technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes.”
Docker is used by 35% of all respondents and 39.2% of professional developers. It is safe to say 1/3rd or more software engineers are using docker. In 2020 and beyond, if you are not using docker as a developer you are missing out for sure.
Node.js on Docker with high scalability #
Node.js was initially released in 2009. It has been used for high traffic web applications by big companies like Paypal, Netflix, Ebay, and LinkedIn to name a few. It has surely been battle-tested in the past 10 years and has proven its mettle.
It also works well with a big team where Spotify is an example. It was used by 90 teams and 600 developers at Spotify. As per W3tech, 1% of websites use Node.js.
1% of the websites tracked by W3tech might seem a small number, but Node.js is popular in websites with high traffic as mentioned above.
With high software scalability in the picture, it becomes a lot easier to scale the application horizontally with Docker and Kubernetes. We can say thet, using Docker with Node.js enables high scalability.
Assumptions for Docker with Node.js #
- You have some familiarity with using Node.js (express js or any other framework)
- You have some experience using Docker (local development, production environments preferred)
- I am using Docker version 19.03.13 and docker-compose version 1.27.4, I hope you have similar versions.
- For the first part of this tutorial, we will use Node.js 18 with npm and npx installed.
Steps #
Let’s dive deeper into step-by-step details of this tutorial on how to run a Node.js express demo application on docker with docker-compose.
1. Setup express with express-generator #
As the first step, it is time to set up a bare-bones Node.js express application. To generate the express js application we will use the express application generator.
1.1 Use express-generator to scaffold the app #
To generate your demo Node.js express application for docker with Node.js, execute the following commands:
npx express-generator --view=pug express-appNotice that we are generating a web app not an API and using pug as the templating engine for the views. It should give you an output like below:
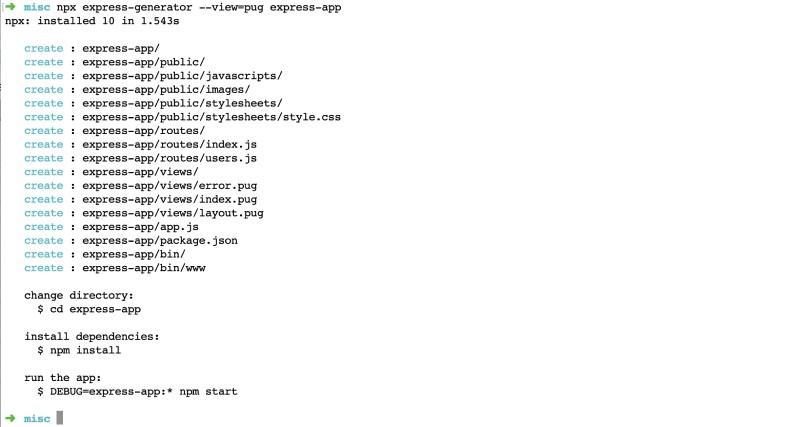
Now, let’s run the app to see how it looks on the browser, no Node.js on docker yet. To start the Node.js express application, please run the following commands:
cd express-app
npm install
DEBUG=express-app:* npm startAfter that, you should see something like below:
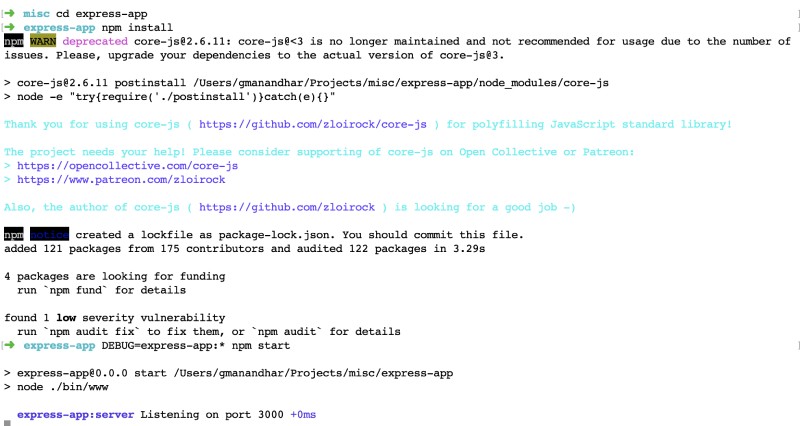
Hit http://localhost:3000 on a browser like Chrome to check if the app is running correctly. You should see something similar to this:
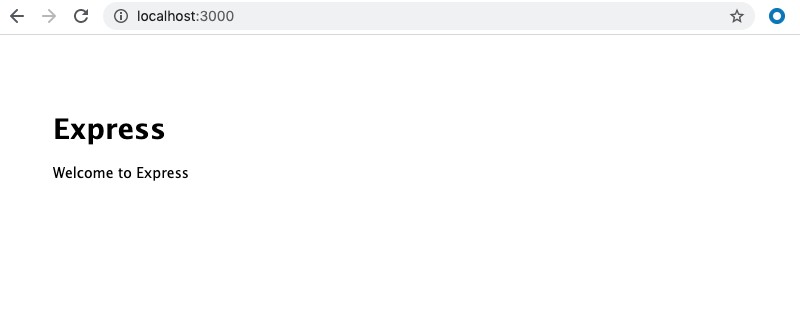
When you hit the homepage on the browser, you will also see some logs on how long the request took to respond on the command line.
At this point, I have added it to git, if you want to view the code it is in this pull request.
1.2 Edit the index to see the changes #
You can edit the page to say something different like Express on Docker and Let’s get started or something of that sort. To do this we will need to edit 2 files, /routes/index.js and views/index.pug, like below. You can get the file changes in this pull request:
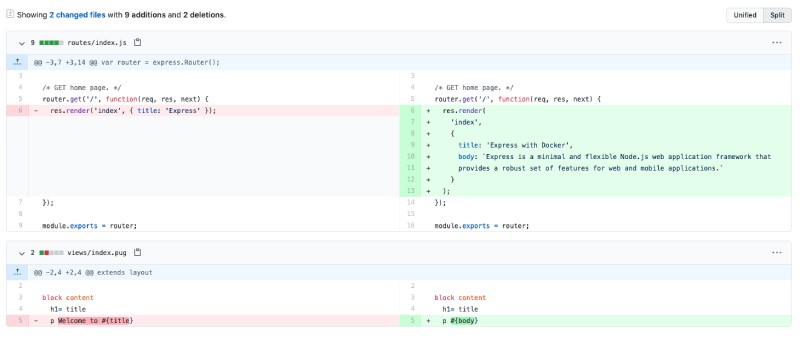
It shows up on the browser like below:
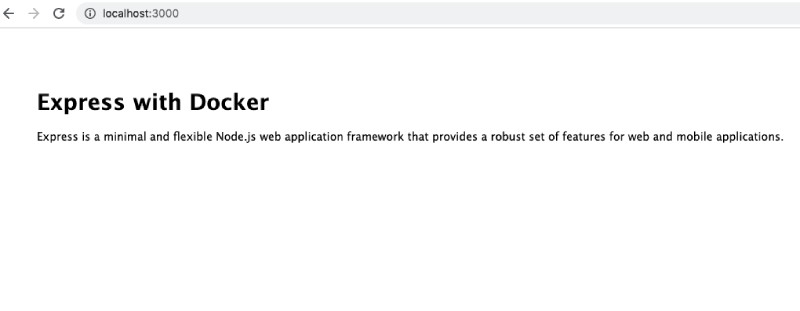
1.3 Add nodemon to monitor changes and reload #
For a better developer experience, it is best to reload the server when a file changes. To achieve this we use nodemon. There are 2 ways to use Nodemon. The first way is to install it as a global node module resulting in a global nodemon command. The second one is to have it as a dev dependency local to the project. We will be using the first way with the following command:
npm install -g nodemon; #if you don’t have nodemon installed
nodemon bin/wwwAfter you run your application index (bin/www in this case) with nodemon it will restart the server on each file save. Below is an example of how it looks on server restarts on code change:
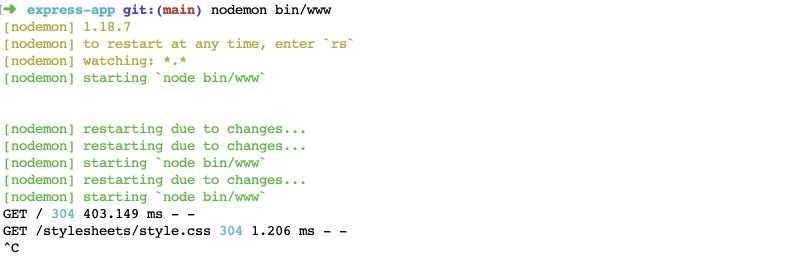
At this stage, you have the generated Node.js express app running. It can also be run with nodemon to restart the Node.js server on every file save. Next stage is to use Node.js on docker.
2. Use Node.js on Docker #
To use Node.js on Docker, we will start with a Dockerfile. As per the Docker’s official website:
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image. Using docker build users can create an automated build that executes several command-line instructions in succession.
We will start with a simple dockerfile and move on to a multi-stage one. We will use a multi-stage build dockerfile so that we have one stage for development and another one for production. In the development stage we will have Nodemon. There will be some optimization for the production docker container, one of them being the absence of not needed Nodemon.
2.1 Simple docker file for local Node.js docker development #
Below is the simple Node Dockerfile for the express application:
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /src
COPY package.json package-lock.json /src/
RUN npm install --production
COPY . /src
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "bin/www"]The dockerfile is simple. It is:
- using
node:18-alpineas the starting point. We are using alpine because it is a small and secure base image for docker containers. - We first copy package.json and lock file to the WORKDIR
/srcto exploit docker’s build caching - Then we run
npm install --productionto get only the needed application dependencies from npm - After that our application code is copied to
/src - Consequently the port is exposed and command to star the server is executed
With good use of Docker caching and BUILDKIT you can get faster docker builds. To build the above dockerfile to a Node.js docker image execute the following:
DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build -t nodejs-express-docker .It will take some time. After it is done you should see an output like below:
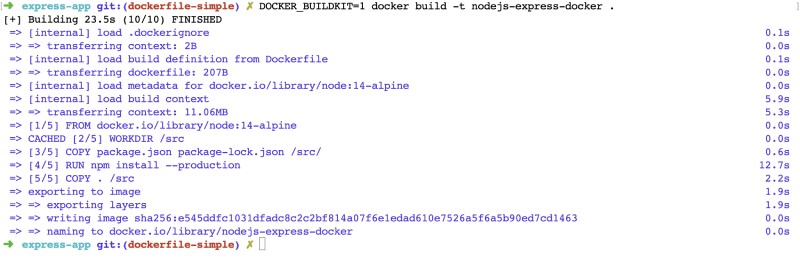
Time to run the docker image and see the output for Node.js with Docker on the browser. To do this run the following command:
docker run --rm --name nodejs_express -d -p 3000:3000 nodejs-express-dockerIn the above command:
--rmis used to remove the container when it is stopped--nameis used to name the container running Node.js on docker, it will be used later to see logs and stop the container-dis used to detach the container process sending it in the background-p 3000:3000means the local post 3000 is mapped to container port 3000
Now to know the container is running, run the following command:
docker psYou should see something like below:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
930b3227688b nodejs-express-docker "docker-entrypoint.s…" 4 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:3000->3000/tcp nodejs_expressYou can view the logs from the container with the following command:
docker logs -f nodejs_expressThis will attach the command line (bash) to the container logs. Then hit the url http://localhost:3000 on a browser. You will see some logs. Hit Ctrl+C to stop viewing logs. Now you can stop the container with the following command:
docker stop nodejs_expressBelow is a recap of running the docker container, viewing logs and stopping it:

This above simple dockerfile is also available as a pull request for your convenience. At this juncture, we can proceed to make the Node.js dockerfile even better with multi-stage docker build.
2.2 Multi-stage docker file to support Nodejs docker in production #
We will create 3 stages from the above simple dockerfile. The stages will be as follows:
- Base: This stage will have things common for docker with Node.js
- Production: This stage will have components useful for production environment for Node.js on docker. It also uses
npm ciin place of npm install. - Dev: This stage will have nodemon which is only useful for developing Node.js on docker
Below is the modified dockerfile:
FROM node:18-alpine as base
WORKDIR /src
COPY package.json package-lock.json /src/
EXPOSE 3000
FROM base as production
ENV NODE_ENV=production
RUN npm ci
COPY . /src
CMD ["node", "bin/www"]
FROM base as dev
ENV NODE_ENV=development
RUN npm install -g nodemon && npm install
COPY . /src
CMD ["nodemon", "bin/www"]You can build the above Node.js dockerfile to run Node.js on docker with the following command:
DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build --target=dev -t nodejs-express-docker-multi-stage .The addition here in this docker build command compared to the above one is the inclusion of --target=dev. It tells docker to build the dev stage not production. If you want to build this multi-stage docker file for Node.js on docker use --target=production and it will create a docker image optimized for production.
To run the Node.js docker image and attach to its logs, you can run the following comamnd:
docker run --rm --name nodejs_express_ms -d -p 3000:3000 -v "$(pwd)":/src nodejs-express-docker-multi-stage && docker logs -f nodejs_express_msThe main difference here from the above docker run command for Node.js with Docker is -v "$(pwd)":/src. As we want the server to restart on every file change the current directory is mounted on the docker container’s work dir. With this on each change the sever will restart for Node.js on docker.
The mulit-stage dockerfile for docker with Node.js can be found in this pull request. Below is a quick recap of the commands for Node.js docker multi-stage build:
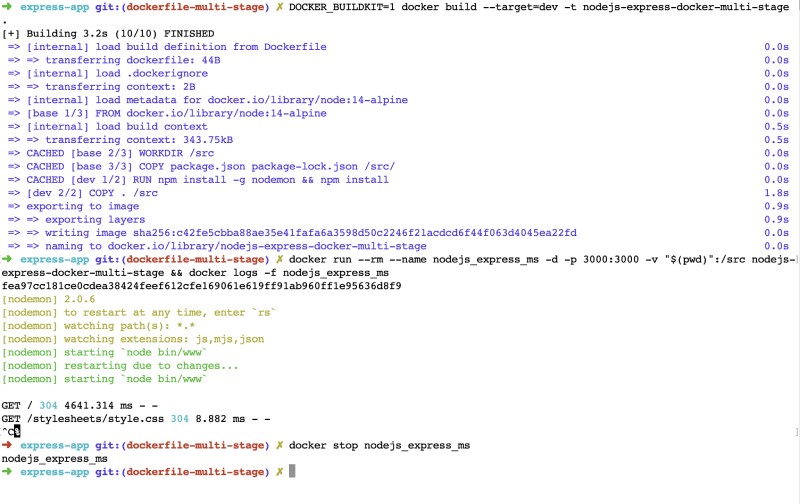
3. Node.js Docker made better with docker-compose #
As seen, we had to run long commands like below:
docker run --rm --name nodejs_express_ms -d -p 3000:3000 -v "$(pwd)":/src nodejs-express-docker-multi-stage It was not easy, to say the least. Stopping the running contianer also needed another docker stop command. The solution to these issue is using docker-compose with Node.js on docker. Docker compose can be used effectively to sew up multiple services like a database with the applicaiton Node.js docker container.
With docker-compose you can get the application running with just as single commands, docker compose up. It will build the containers if they are not built and run them for you. Next, we will see how to do it.
3.1 Build the Node.js docker-compose with dev target #
To being with, below is the docker-compose.yml file that can run the applicaiton on docker with Node.js using docker-compose:
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
build:
context: ./
target: dev
volumes:
- .:/src
command: npm start
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
NODE_ENV: devThe docker compose file has some parts to understand:
- The version is latest at
3.8 - In services, the web service has
target:devbeing sent so that we build only for the dev stage not production - The current directory
.is mounted to the docker container at/srcso the changes will be reflected in the container too. - We changed the
npm startcommand in the Docker with Node.js to usenodemonas we wil use docker compose only for development. - We pass in only one environment variable
NODE_ENVasdevother environment variables for instance database credentials can also be passed in as environment variables. In this tutorial, you can learn more about docker compose environment varaibles and ways to pass it.
We will be using BUILDKIT to build docker containers with docker-compose too. To use BUILKIT with docker-compose while building the docker container we can execute the command below:
COMPOSE_DOCKER_CLI_BUILD=1 DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker-compose buildHere you see the output of the docker-compose build for docker with Node.js with BUILKIT in action:
3.2 Run the Docker with Node.js using docker compose up #
After the containers are built it can be easily run with docker-compose up.
After the Node.js docker containers are built, it can be run with docker-compose up like below:

The changes for docker-compose addition is in this pull request. This is how you can run Node.js on Docker which works very well for Developing as well as putting the containers in production environment.
TLDR; Give me a quick run down #
All the code is in a public github repository. You can run the following commands to get started quickly:
- Given you have git setup correctly, clone the repo with:
git clone [email protected]:geshan/express-app.git - Then execute
cd express-app - After that run
COMPOSE_DOCKER_CLI_BUILD=1 DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker-compose build, wait for build to finish. - Consequently execute:
docker-compose up, wait for some time to seenodemon starting...on your console. - Following that, hit
http://localhost:3000on a browser - You should see the following output on your browser:

Enjoy! Now you can reverse engineer the Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml file. If you have any questions, search for specific thing like say target in this post.
Considerations #
There are some considerations you should be aware of:
- In my expreience, containers on production is run with an orcherstrator like Kubernetes. I believe Docker Swarm (and docker compose) in produciton have lost the race by now.
- It is best to use Docker build caching and BUILDKIT for faster builds.
- Docker compose makes it easier to use multiple dependency on development environment. For exmaple if you application depends on MySQL and Redis it can be easily put together in the
docker-compose,ymlfile.
Conclusion #
Using Node.js on Docker is a rewarding experience. If you want to upgrade Node.js, it is as simple as changing the version on the Docker file, rebuilding it and using it. Node.js is also great for microservices.
If you want better developer experience and amazing scalability on production with ease, start using Node.js on docker today.
