If you are developing any Node.js application, nodemon is one of the necessary weapons in your arsenal. Learn how to install and effectively use nodemon to automatically restart your Node.js application on every relevant file change. Do you want to restart your Node.js web server and save loads of development time? In this post, we are going to see how you can utilize Nodemon with any Node.js application easily.

Table of contents #
Nodemon a quick intro #
Having Nodemon to watch your file changes is like having an eagle watching over its prey.
On every file save and your Node.js server is automatically restarted for you as easy as that.
Even Nodemon’s slogan says “reload, automatically”. It might come to you as a surprise that Nodemon can be used with other languages like Python, Ruby, or even make as well. Nodemon is used as a dependency by more than 1.5 million projects, so it is surely battle-tested. If you are not using Nodemon for development, you are suffering.
Let’s go ahead and install nodemon.
How to install nodemon? #
Before we install nodemon, we will use a sample app to see nodemon in action. We will use Node.js MySQL open-source application that I have used for the Node.js MySQL tutorial post. This is a simple quotes REST API built with Node.js, Express.js communication with a MySQL database. Next, we will install nodemon in this sample application.
Like most npm modules, Nodemon can be installed in two ways as follows:
Install nodemon as a global dependency #
To install nodemon as a global NPM dependency we can run the following command:
npm install -g nodemonThis will install nodemon as a global dependency. It will also make the nodemon command available on any path you run it on. The advantage is that you don’t need to install nodemon on each of your Node.js projects.
Install nodemon as a local project dependency #
For installing nodemon as a local project NPM dependency, we can execute the following on the project we want:
npm install --save-dev nodemonFor our sample project, we are going to run the above command. Running it should show us something like below:
As we used --save-dev, nodemon has been added to the devDependencies section of the package.json file. Similarly, relevant changes have been added to the package-lock.json file too. If you use yarn you can run yarn add nodemon --dev to add nodemon to your devDependencies.
When we install nodemon locally, you will not have access to the nodemon command everywhere. If you run nodemon outside of the package.json context you will get the nodemon command not found problem. To tackle this you can install nodemon globally.
You can view the changes of adding nodemon as a dev dependency using NPM in this pull request.
How to use nodemon? #
To use nodemon we will replace the node command with nodemon command when we run our app. Now as we have nodemon installed as a local dependency, to make things easier we will add a new script in package.json to run the application with nodemon. We can add the new script in the package.json file as below:
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./bin/www",
"start:dev": "DEBUG=nodejs-mysql:* nodemon ./bin/www"
},After that, we can run the app with the command npm run start:dev and hit http://localhost:3000/quotes to see the output on the browsers. As we have the app running with nodemon, if we change any file and save it it will rerun the command after nodemon again. For example, I added a , in a line in src/services/quotes.js and saved the file which resulted in:
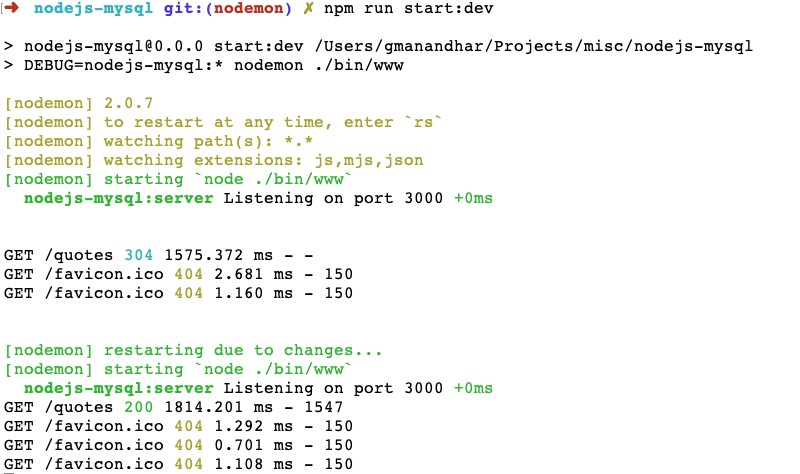
As seen above, the Express.js server restated on each file change as expected.
More Nodemon configs #
We can add more configs by passing more parameters to the nodemon command or adding a nodemon.json file. For example, if you want to make nodemon work well with docker you will need to add --legacy-watch or -L so that it enables Chokidar polling and nodemon will work with docker. You can have a look at Node.js with Docker example too.
You can even delay restarts for nodemon using the --delay parameter like:
nodemon delay 2 index.jsThis will wait for 2 seconds before restarting the server on file changes. If you want to watch say .js and .sql files you can do it with the following command:
nodemon -e js,sql index.jsDepending on what we want to do, we can add more configs on a nodemon.json file. Below is an example of a nodemon.json file:
{
"events": {
"start": "clear"
},
"delay": "2500"
}The above nodemon.json will make sure that on each restart the clear command is run which will clear any old console output. Similarly, it will also restart the server after 2.5 seconds of a file change. We can add other configs too like file extensions, files to ignore. These configs can be put into the package.json file too under the nodemonConfig index in that file. Here is another sample Nodemon.json file from the nodemon repo.
I would highly recommend you to read the nodemon docs. The FAQ of nodemon is a great place to find answers to any issues you are facing with nodemon. There are answers to issues relating to Docker, windows, and permission to name some of them.
You can find the nodemon command the sample config file in this pull request.
If you need more docs or help for nodemon usage, you can run ./node_modules/nodemon/bin/nodemon.js -h if nodemoe is installed locally. If nodemon is installed globally you can simply execute nodemon -h and see the help.
Conclusion #
We have seen that nodemon is a very useful tool for Node.js development. Be it a web server, a command line interface (CLI) command or any other workload nodemon will make your life a lot easier.
Nodemon is like having someone restart your servers for you on every file change. It is very handy when writing web applications because it makes testing a lot more frictionless.
I hope you have learned how to use Nodemon to automatically restart your Node.js application with this quick tutorial.