Docker has shot up in popularity over the years. Postgres (a.k.a PostgreSQL) is an open-source, standards-compliant, and object-relational database been developed for more than 30 years now. This official feature matrix shows the wealth of features Postgres has.
Running Postgres with Docker and docker-compose makes it very easy to run and maintain especially in a development environment. In this post, we will look into how to run and use Postgres with Docker and Docker compose step-by-step keeping things simple and easy. Let’s get started!

Table of contents #
- Why use Postgres with docker for local development
- Prerequisites
- Postgres with Docker
- PostgreSQL with docker-compose
- Adding Postgres with Docker to an existing Node.js project
- Conclusion
Why use Postgres with docker for local development #
There are many good reasons to use any database like Postgres with Docker for local development, below are some good reasons:
- Using multiple versions of PostgreSQL as per project or any other need is very easy.
- Generally with docker if it runs on your machine it will run for your friend, on a staging environment and production environment given the version compatibility is maintained.
- When a new team member joins, the new member can get started in hours, it does not take days to be productive.
You can read more about this on why to use docker. In the following section, we will look into some good to have things before diving into the commands to run Postgres with Docker.
Prerequisites #
Before we dive into some CLI commands and a bit of code below are some prerequisites best to have:
- Basic knowledge of Docker will be helpful like executing commands like docker run, execute, etc. For this tutorial, docker version 20.10.10 will be used in a Mac.
- Any prior grasp on Docker compose would be useful but not necessary. For this guide, we will use the docker-compose version 1.29.1 on a Mac.
- An intermediate understanding of how relational databases work, especially PostgreSQL would be highly beneficial.
- We will use an existing application/API with Node.js and Postgres replacing a remote Postgres with a local one running with Docker and Docker compose, so it would be advisable to read the previous post about it.
Given the prerequisites have been mentioned we can move forward to the next section where we will run some docker commands. Get those itchy fingers ready now.
Postgres with Docker #
For this post, we will use the official Postgres docker alpine image from DockerHub. We will be using the latest version 14.1 of PostgreSQL.
The default bullseye version of Postgres docker image is 130 MB whereas the alpine one for the same version is 78 MB which is a lot smaller.
To simply run the container using the Postgres 14.1 alpine image we can execute the following command:
docker run --name basic-postgres --rm -e POSTGRES_USER=postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=4y7sV96vA9wv46VR -e PGDATA=/var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata -v /tmp:/var/lib/postgresql/data -p 5432:5432 -it postgres:14.1-alpineLet’s evaluate what the above command does. It tries to run a container from the posgres:14.1-alpine image which will be pulled in from Dockerhub by default if it does not exist.
First, the name basic-posgres is given to the running container, and --rm will clean up the container and remove the file system when the container exits. Some environment variables have been added to make things easier.
The last 3 parameters are interesting, -v adds a volume to store data, for this example, it has been mapped to /tmp so all data will be lost when the machine restarts. Next, we use the -p parameter to map the host port 5432 to the container port 5432.
The last parameter to the command is -it to have the tty available. When we run the command we will see an output like the below:
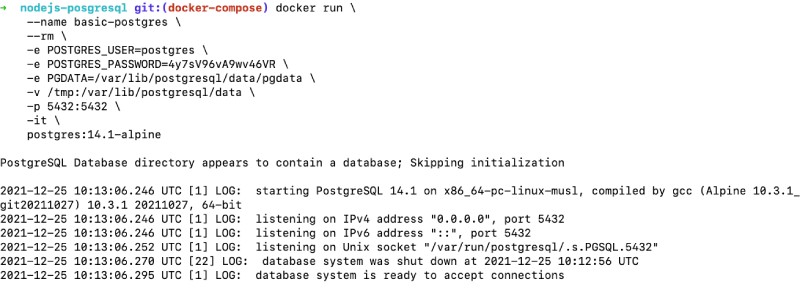
The container is running and ready to accept connections, if we run the following command we can go inside the container and run the psql command to see the postgres database which is the same as the username supplied in the event variable.
docker exec -it basic-postgres /bin/shAfter we are inside the container we can run psql --username postgres to access the Postgres CLI. To list the databases we can run \l inside the psql CLI to list the databases and see the Postgres database as seen below:
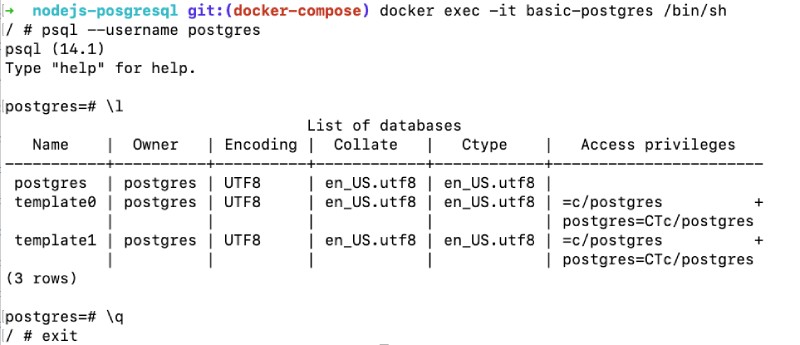
As seen in the above picture \q will quit the psql CLI and exit the container’s shell we have ran exit.
If we go back to the running container and hit Ctrl+C it will stop the container as well as clean it up as we have used the --rm parameter when we ran it.
This is a way to run Postgres with docker but as we have seen it is not easy to remember the 10 liner command and all the needed parameters.
Also, we have not specified any link between the database and our application. This is where the docker-compose file and docker-compose command comes in very handy as seen in the next section.
PostgreSQL with docker-compose #
To run the same Postgres 14.1-alpine with docker-compose we will create a docker-compose-pg-only.yml file with the following contents:
version: '3.8'
services:
db:
image: postgres:14.1-alpine
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
ports:
- '5432:5432'
volumes:
- db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
db:
driver: localThe docker-compose file has the following things to consider:
- It uses the docker-compose file version 3.8
- Next up, we define
dbas a service, each service will equate to a newdocker runcommand - We are asking docker-compose for the service to be an image of Postgres version 14.1 alpine which will always restart if the container stops automatically.
- Consequently we define two environment variables to send in the Postgres user and password. Keep in mind, as the database is not sent by default for the official image it will use the username as the database name.
- Subsequently we map the host/machine port
5432with the container port5432as Postgres runs in that port in the container. - After that we ask docker-compose to manage the volume in a name called
dbwhich is further added to be a local driver. So when the container is restarted the data will be available from docker managed volume. To see the contents of the volume we can rundocker volume lsand inspect the volume attached to our Postgres container.
After that explanation, to start the containers we will run docker-compose -f docker-compose-pg-only.yml up which will show an output like below:
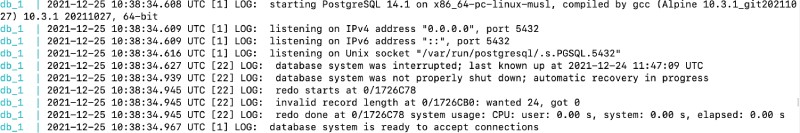
So the Postgres database is running and this time it was a one-line command, not a long command to get it running as all the needed parameters were in the docker-compose file.
At this point, the Postgres in the container will behave similarly to a local Postgres instance as we have mapped the port 5432 to the local port 5432.
Next up, we will see how we modify the docker-compose file to fit in an existing project.
Adding Postgres with Docker to an existing Node.js project #
Given we have seen PostgreSQL run with docker-compose, now we will integrate it with a running Node.js API project. A full step-by-step tutorial of how this Quotes API project is built with Node.js and Postgres is available for your reference. For this guide we will add a docker-compose.yml file with the following contents:
version: '3.8'
services:
db:
image: postgres:14.1-alpine
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
ports:
- '5432:5432'
volumes:
- db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./db/init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/create_tables.sql
api:
container_name: quotes-api
build:
context: ./
target: production
image: quotes-api
depends_on:
- db
ports:
- 3000:3000
environment:
NODE_ENV: production
DB_HOST: db
DB_PORT: 5432
DB_USER: postgres
DB_PASSWORD: postgres
DB_NAME: postgres
links:
- db
volumes:
- './:/src'
volumes:
db:
driver: localThis file looks somewhat similar to the above docker-compose file but below are the main differences.
The first one is, here we use - ./db/init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/create_tables.sql on line number 13. We are doing this to create the quotes table and fill up the data as seen in this SQL file. This is the way to run initialization scripts for Postgres with docker. This is an idempotent operation, if the data directory is filled up the init.sql file won't be executed again to prevent data overriding. If we want to force override the data we will need to delete the docker volume after a docker volume inspect.
Next, we define a new service called api which builds the local Dockerfile with target production and names it quotes-api. After that, it has a depends_on definition on the db container which is our Postgres container.
Subsequently, it maps the host port 3000 to the exposed container port 3000 where the Node.js Express API server is running. In the environment variables, it defines db as the host which maps to the above Postgres container and uses the same credentials as provided in the above definition. It links to the Postgres container defined before the API service. You should learn more about docker compose environment variables.
Finally, it maps all the local files to the /src of the container to make things run with Node.js.
This file is available on GitHub too for your reference.
When we run docker-compose up on the root of this project we can see the following output:
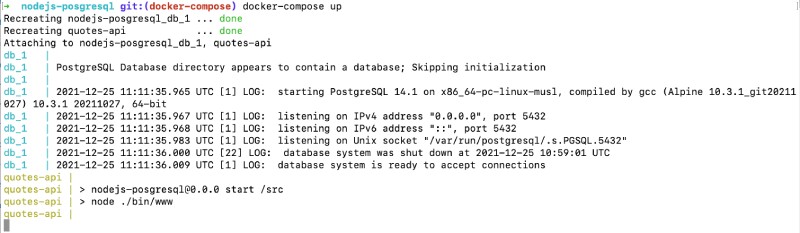
As the webserver is mapped to the local port 3000, we can see the output as below when hitting http://locahost:3000/quotes on any browser:
Hurray! Our Node.js Express API for Quotes is communicating correctly with the local Postgresql database as expected. If you want to quickly try the docker-compose up experience clone this Github repository and try it.
If Node.js with MySQL is your flavor of choice do read this guide too. You can also try Node.js with SQLite if that works better for you.
Conclusion #
In this post, we witnessed how to run Postgres with just docker then added the docker-compose goodness to make things easier. After that, we added Postgres to an existing Node.js API to make the local development a lot easier.
I hope it makes it easier to understand how to run Postgres with Docker quickly and easily.
