Comma-separated values more commonly known as CSV has been used for a long time as a standard text-based way to represent and transfer data. There are many ways to read and write CSV files in Node.js. In this post, we will learn how to read a CSV and write a CSV file using Node.js in an efficient way. Let’s get rolling.

Table of contents #
- More on CSV
- Options to read and write CSV in Node.js
- Fast CSV to read CSV files in Node.js
- Write CSV in Node.js with Fast CSV
- Popular npm packages for CSV
- Conclusion
More on CSV #
A CSV file is a plain text file that contains data formatted as per the CSV standard. Every line represents a record and each field in the record is separated from the other using a special character which is comma , in the case of CSV. It is easy to represent tabular data in CSV. Below is a snippet of COVID-19 vaccination data about NSW suburbs:
State,Suburb,2019 ERP population,% Vaccinated - Dose 1,% Vaccinated - Dose 2
New South Wales,Albury,"52,067",>95%,>95%
New South Wales,Armidale,"31,679",92.4%,88.9%
New South Wales,Auburn,"86,994",94.1%,91.0%
New South Wales,Bankstown,"147,237",93.3%,89.9%
New South Wales,Bathurst,"39,532",>95%,93.0%
New South Wales,Baulkham Hills,"124,066",>95%,>95%
New South Wales,Blacktown,"115,631",>95%,>95%
New South Wales,Blacktown - North,"85,385",>95%,>95%
New South Wales,Blue Mountains,"64,747",>95%,>95%
New South Wales,Botany,"45,823",>95%,>95%
CSV files are used for many things, one of the prominent usages is for data import and export. Even if there is no UI created for a particular new system, data can be imported in the form of CSV mainly taken out of some spreadsheet program. This can be used as a quick start to get needed data into the system.
Similarly, CSVs are great to export data out of some tables/reports. They act as a starting point that can be opened up in a spreadsheet program to do further data analysis. Undoubtedly, Node.js can be used to both parse and create CSV files, we will delve into the options in the following section.
Options to read and write CSV in Node.js #
There are multiple NPM packages to read and/or write CSV files with Node.js. The most popular one is Fast CSV, it is a mix of fast-csv/parse to read CSV files and fast-csv/format to format and write CSV files. Some other options include csv-parser, csv-writer, neat-csv and csv to name some. Details about the popularity in terms of download is discussed towards the end of this piece. It would be a good time to take a refresher on how to read file line by line in node.js if that interests you.
All the code below will be run on Node 18 and it is expected that you know how to install npm packages with npm install. Let’s look at how to use Fast CSV to read an existing CSV file with Node.js next.
Fast CSV to read CSV files in Node.js #
Reading an existing CSV from the file system or a CSV uploaded by the user is quite easy. In the example below, we will see how to read a CSV file from the file system which has ~85K records of all the confirmed COVID-19 cases in Australia by suburb as seen in this CSV file:
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const { parse } = require('fast-csv');
let rows = [];
fs.createReadStream(path.resolve(__dirname, 'confirmed_cases_au_by_location.csv'))
.pipe(parse({ headers: true }))
.on('error', error => console.error(error))
.on('data', row => {
console.log(row);
//each row can be written to db
rows.push(row);
})
.on('end', rowCount => {
console.log(`Parsed ${rowCount} rows`);
console.log(rows[81484].postcode); // this data can be used to write to a db in bulk
});Let’s analyze the code a bit now. First, we require the native fs and path modules. Then we require the parse function from fast-csv npm package. After that, we create an empty array called “rows” where we will put in all the rows read from the CSV file.
Next up, a readable stream is created from the file and piped to the parse function with headers true. The headers true value means to parse the header information from each row. In case of any error, it is shown in the console, and on each row, we are logging the row and pushing it to the rows array as well. When the reading ends, we console.log the number for rows parsed and the postcode from the last row. The above code can be referenced on Github too.
This data could easily be written to MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite database using Node.js. We can run the above script with time node read-csv.js which will end with the following output:
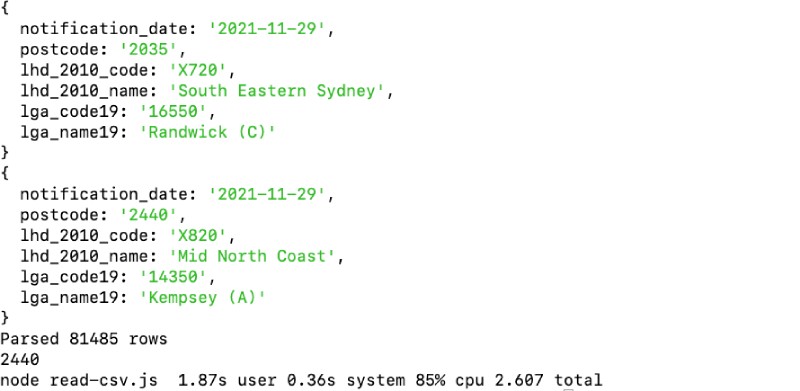
As seen above the script took only 1.87 seconds to read 81485 rows and print them on the screen too. Consequently, we will look at how to write a CSV file with Fast CSV.
Write CSV in Node.js with Fast CSV #
To write a CSV file using Fast CSV we will use the format package included in the Fast CSV npm module. Below is a quick example where we write 80K random rows to a test CSV file which could also have been data pulled in from a database:
const fs = require('fs');
const { format } = require('@fast-csv/format');
const fileName = 'randoms.csv';
const csvFile = fs.createWriteStream(fileName);
let randoms = [];
const min = 1;
const max = 90000;
const noOfRows = 80000;
const stream = format({ headers:true });
stream.pipe(csvFile);
for(i=0; i<noOfRows; i++) {
randoms.push({
characters: Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 7),
number: Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min)
});
stream.write(randoms[i]);
}
console.log(randoms[79999].number);//with randoms array, all data could have been written at the end too
stream.end();
console.log(`${fileName} written with stream and ${noOfRows} rows`);Upon checking the code further, we can find out what is being done. First, the native file system (fs) module is required. Then, the format method from fast-csv/format is also included. Subsequently, we define two variables one for the filename and the other one is a writable stream that points to a CSV file.
Consequently, we define some more constants that will help us generate a random array of objects with 80K random strings and numbers as seen in the above loop. Before generating the number we pipe the CSV stream to the csvFile which means each time we write anything to the CSV stream it will also be written to the file.
Finally, we console log the random number from the last row and end the stream. Then we also console log the filename and number of rows the example CSV file has. The above file is also available on Github.
When we run the above script with time node write-csv.js it renders the following output:
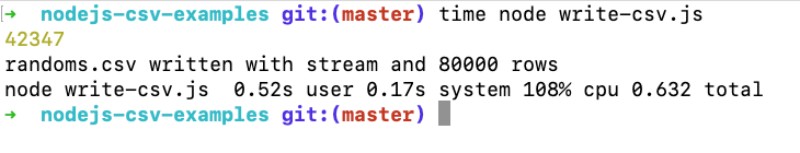
As seen above, the script took only 0.52 seconds to write a CSV file with 80K rows with randomly generated values. It was fast also because of the use of streams.
All the above code is available as a public GitHub repository for your reference.
Popular npm packages for CSV #
Fast CSV is surely not the only package to parse and write CSVs, there are other packages too. A quick comparison on NPM trends for 5 popular CSV packages show the following results:
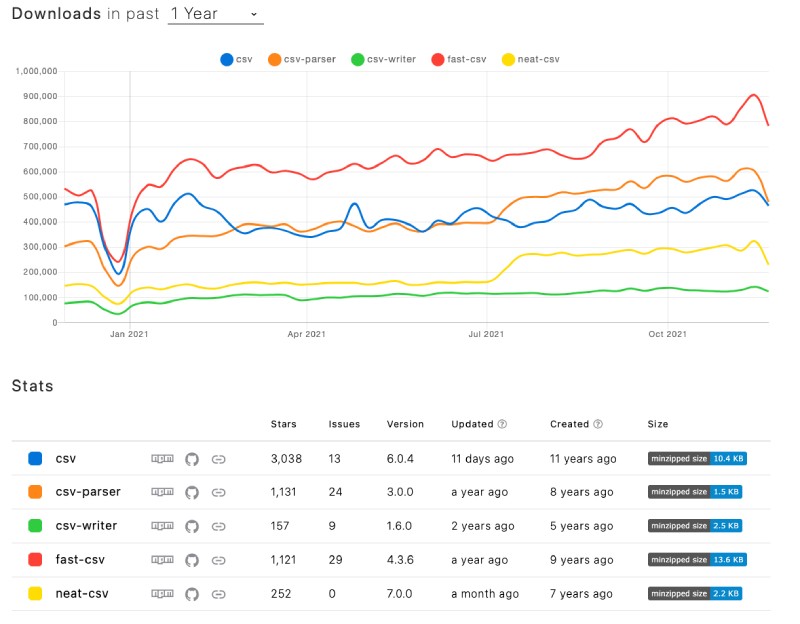
Fast CSV has more than 900K downloads a week that is one of the most popular options to work with CSV in Node.js. CSV parse which is not compared here has more than 1.8 million downloads a week, still, it is not super easy to use as Fast CSV but surely has a host of other features. The choice of the right package can be left on the needs of the project.
Conclusion #
We have seen how to read and write CSV files using Node.js with the Fast CSV npm module. With less than 50 lines of code in total, we were able to read and write relatively big CSV files using Node.js in under 2 seconds which is pretty good.