Can you code and deploy a basic but functional app with minimal coding experience? With the latest Google AI Studio feature, you can build and deploy apps by instructing an agent in minutes. You can also deploy the app on Google Cloud Run and make changes easily. This post will show you how. Let’s get started!
Table of contents #
- The goal
- Build an app with a prompt on Google AI Studio
- Deploy to Google Cloud Run
- Making a change and redeploy
- Conclusion
The goal #
Your goal is to build a Gen AI (LLM)- powered application that will take an image (of a popular place) and then give you back the Country, City, state, place, and the geolocation coordinates of that place. A creative use of this can be stalking and knowing where your friends went by using their Instagram photos. Other usages are up to you. This is more of a proof-of-concept fun project to demonstrate the power of LLM and Gen AI with Gemini 2.5 models.
Build an app with a prompt on Google AI Studio #
Go to Google AI Studio, then click on the Build link in left menu as shown below:
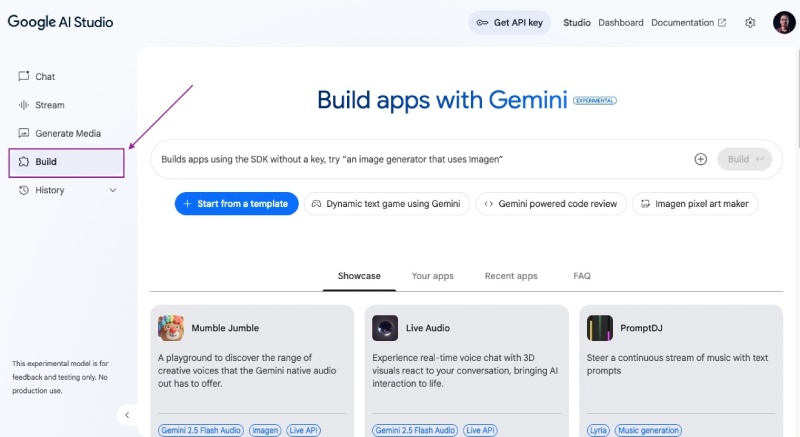
Then paste the following in the prompt text area;
Build an app that can guess Geo location from a given image:
You are an OSINT investigator. Your job is to geolocate where the photos are taken.
Provide the country, region, and city name of the location.
Please pinpoint the exact location with latitude and longitude where the photo was taken.
Could you always explain your methodology and how you concluded?
Provide steps to verify your work.
Also, mention the percentage of how sure you are of the place you have identified it to be
and add a Google Maps link to the exact location
It will look something like the below:
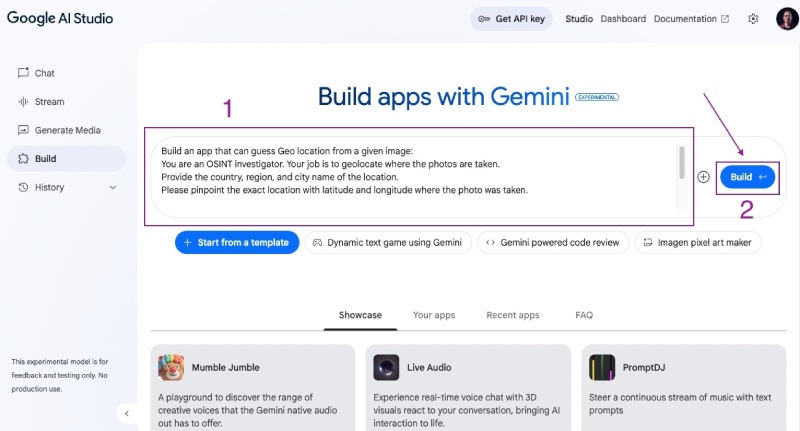
After that, click the blue Build button. It will use a code agent/assistant like Google Jules AI and start “thinking” and writing the whole application as seen below:
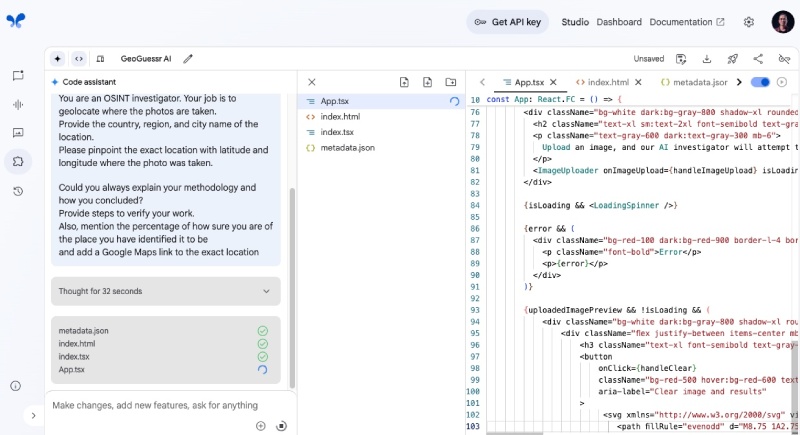
It will take a couple of minutes (or a bit longer), and then it will generate the full app in React and TypeScript. It uses Tailwind CSS for styling. When the app generation is complete, it will look as follows:
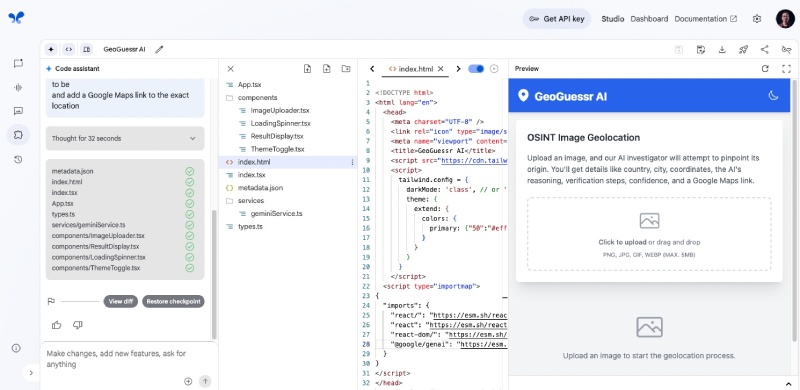
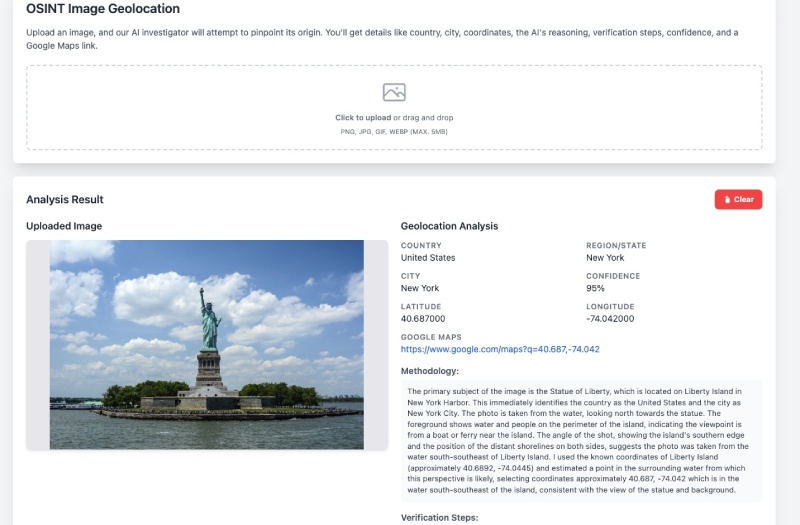
The application preview is available on the right panel, so you can upload and test a picture like this one (Statue of Liberty). It will analyze the photo and guess the geo location as follows:
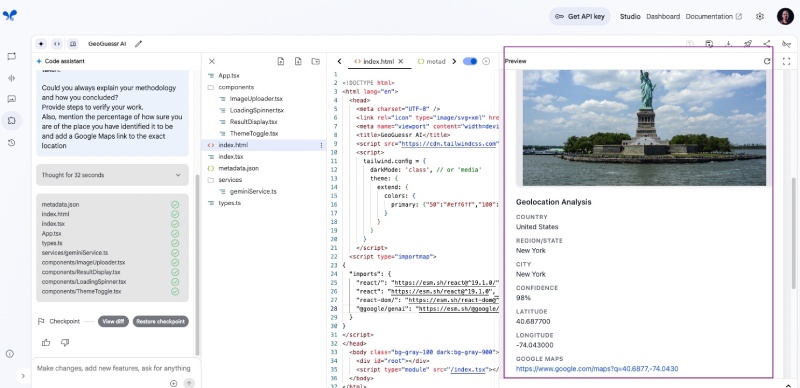
You can even click the provided Google Maps link and see where the place is. You can scroll down to see the methodology and the verification steps as seen below:

In the next section, you will deploy the generated (vibe-coded) app to Google Cloud Run.
Deploy to Google Cloud Run #
Google Cloud Run is a fully managed compute platform that automatically scales your stateless containers. It is a great way to deploy your applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
You will need an existing project and some credits in your Google Cloud Account to deploy to Google Cloud Run. If you do not have an existing project on Google Cloud, you can create a new one as seen below:
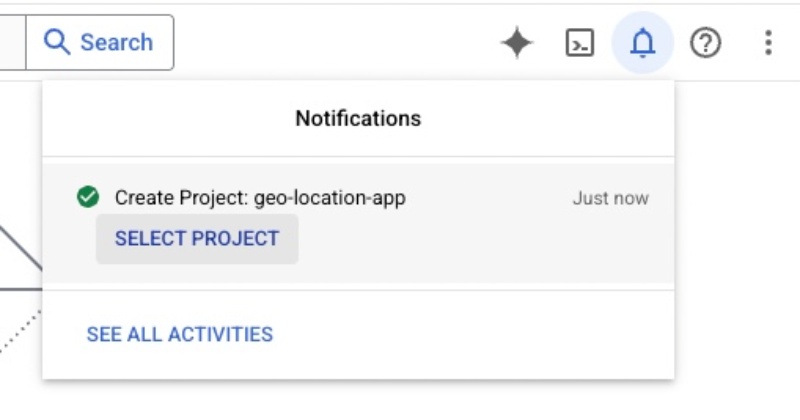
It will take some time, and the project will be created; you will be notified of that. In my case, the project name is geo-location-app, and it will look like the following:
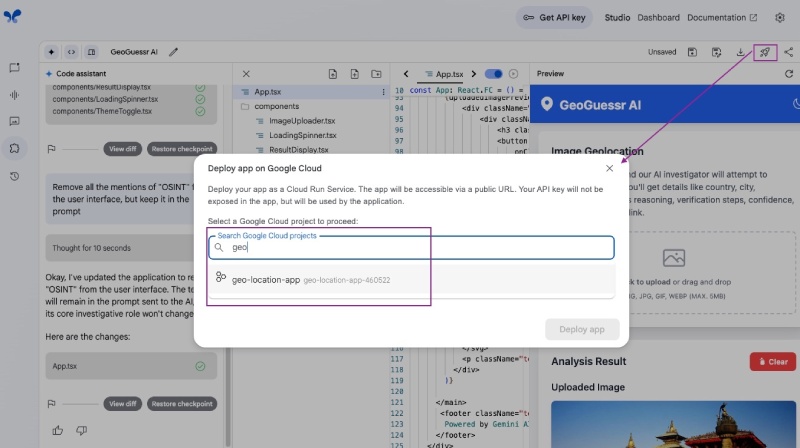
To deploy the generated (vibe-coded) application that you have tested. Go back to the Build page of the generated app. In the Preview section on the right, click the Rocket (🚀) black and white icon on the top right corner above Preview:
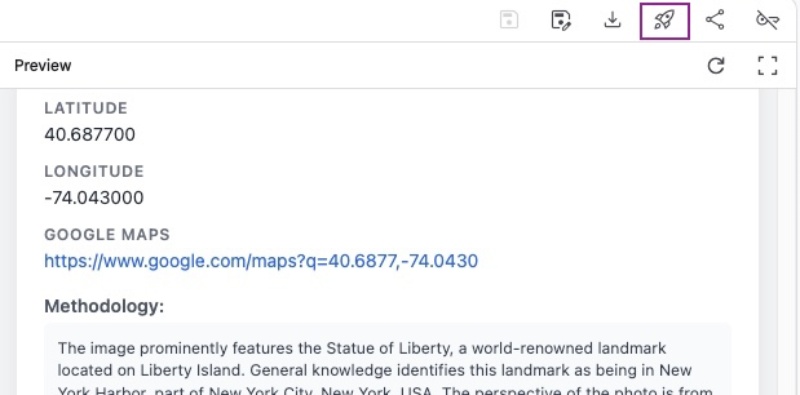
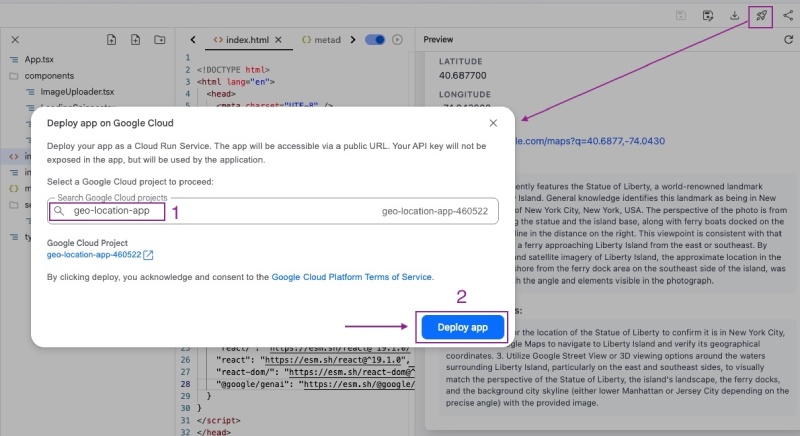
Then, search and select the project you just created on Google Cloud Console, in my case it is geo-location-app, then click the Deploy app blue button as follows:
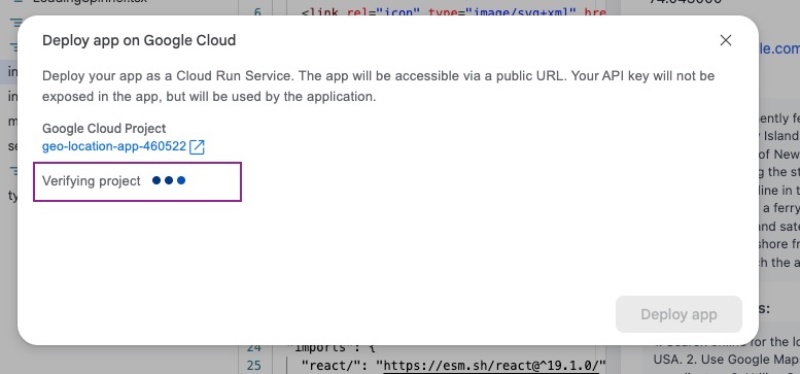
It will take some time to deploy the React App on Google Cloud Run, starting with verifying the project:
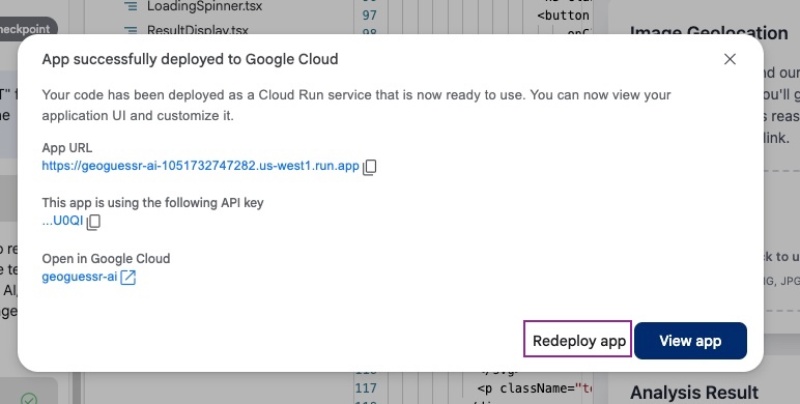
Then it will show Deploying to Cloud Run and finally give you a link to try out your Geo location guessing app, as seen below:
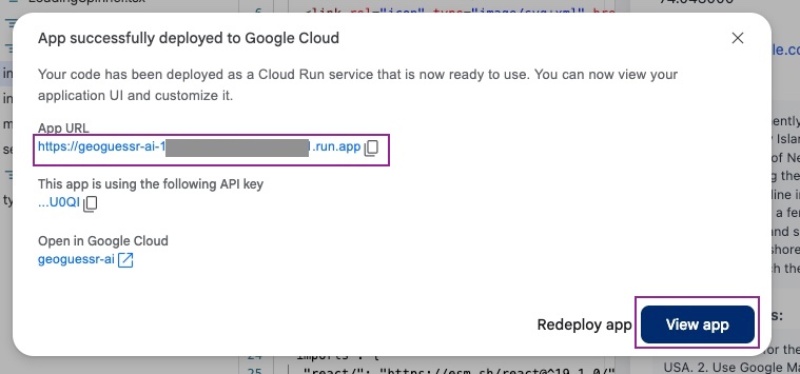
You can click the App URL link or the View app button to see the app working on a publicly accessible URL, the same as the one you tested in the preview. When you click the View app blue button, you will see the app in action:
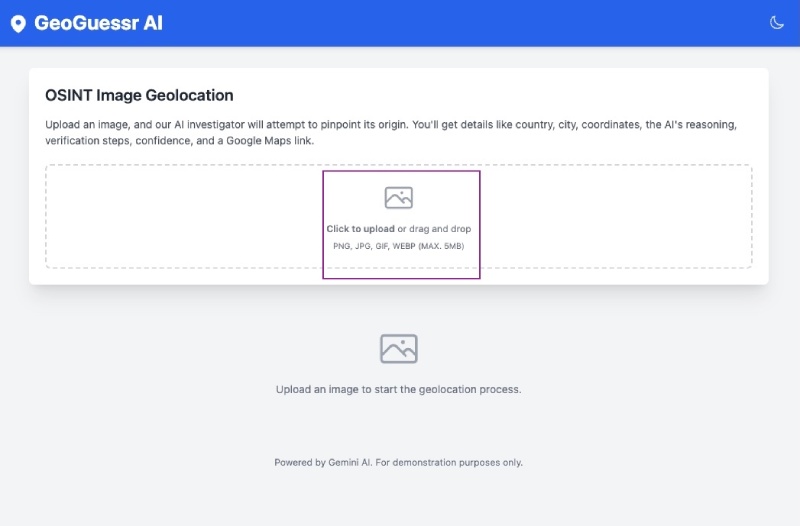
You can upload the same Statue of Liberty photo or any other famous landmark and see how it works:
You can also upload a picture of the Eiffel Tower, and it will guess the location as Paris, France. Give it a shot. You can also switch from light to dark theme and back.
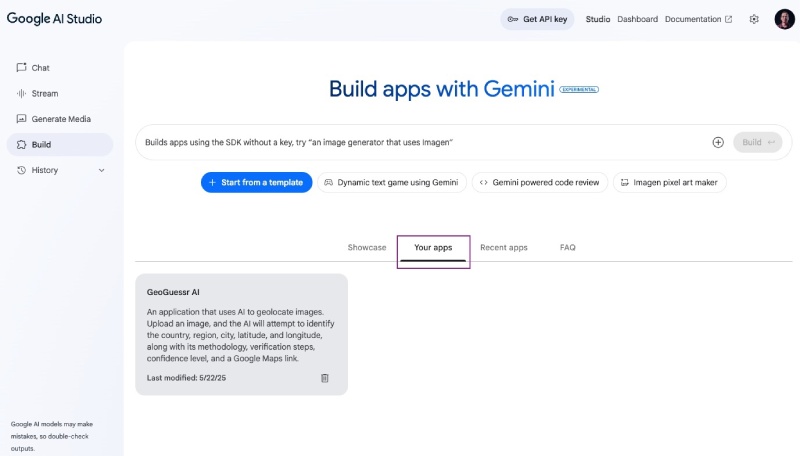
Your app is auto-saved and you can find it in the Your Apps tab in the Google AI Studio’s Build page:
Next, you will learn how to make a change and redeploy the app to Cloud Run.
Making a change and redeploy #
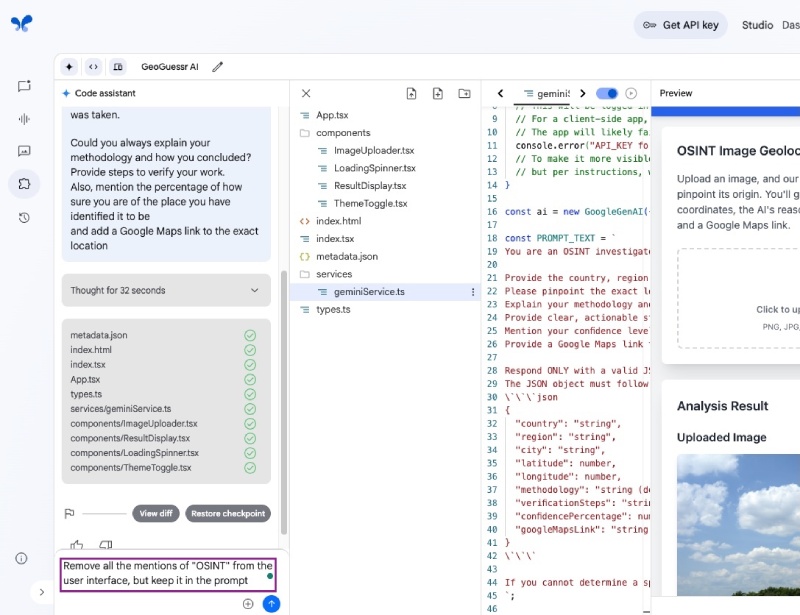
You can make a change to the app and redeploy it. In my case, I want to remove the mention of OSINT from the interface, and I will instruct/vibe code the Code assistant section of the app with:
Remove all the mentions of "OSINT" from the user interface, but keep it in the prompt
You can input the new instruction as follows and hit the blue up button as seen below:
It will take some time to do the given task, after some thinking (in my case, 10 seconds), it started editing the files. The app looked like the following after the change was made:
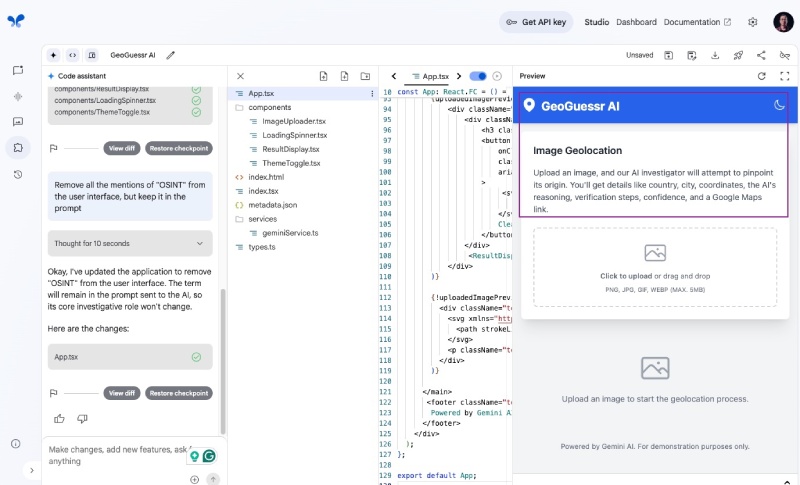
As the change has been made and the app has been tested in preview. You can save the new change by hitting the save icon above the preview. You can redeploy it to Google Cloud Run. To do this, click the Rocket (🚀) black and white icon on the top right corner above Preview and select the same project (it was geo-location-app in my case):
It verifies the project and, given that the app is already deployed in that project, it gives you a Redeploy app link, which you can click to redeploy the change to Google Cloud Run:
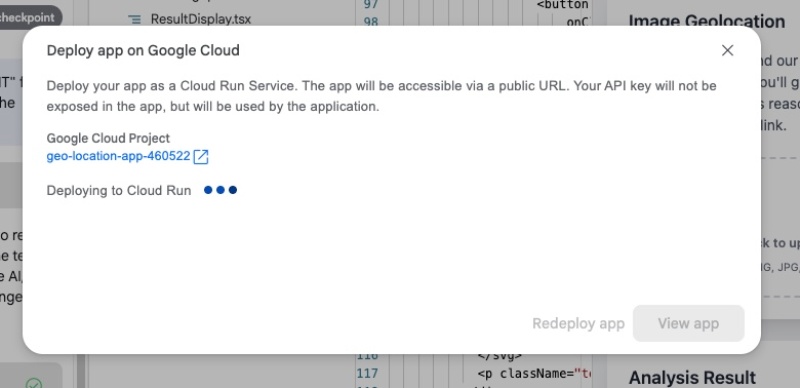
It will take some time to redeploy the app, and you will see the Deploying to Cloud Run message.
It will redeploy the app and give you the same link to the app, which you can test and verify that the change has been deployed and released. After you click View app, I can see that the update has been done:
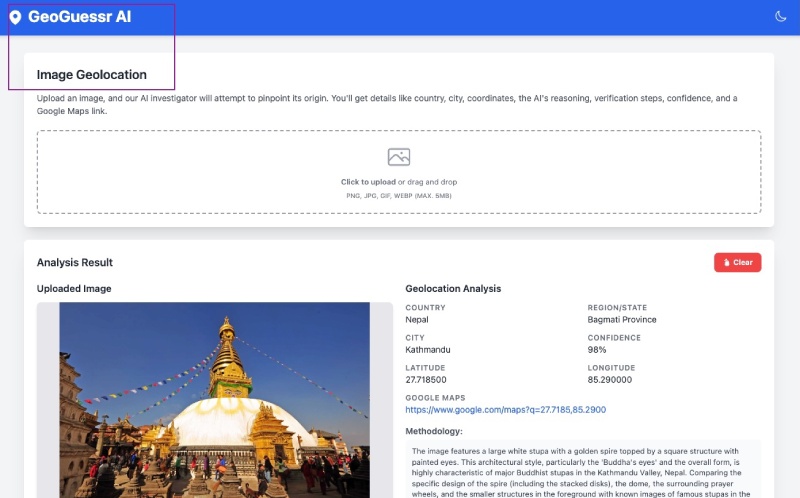
After the change, I tested the app to ensure it worked as expected. There is no mention of OSINT anymore, which is what I wanted. Google Cloud credits are provided for this project. Thanks to Google.
There you have it—you vibe coded a fully functioning app that started with a simple idea and a single prompt. You also deployed it on a publicly accessible URL, which you can share with friends. As it is running on Google Cloud, it will cost you money, so be sure to check your costs on Google Cloud Billing and stop the app if you need to. After testing, you can delete the project with the app running on Google Cloud Run.
In my case, the primary prompt and calling the API were in the services/geminiService.ts file, which was using gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17 with a pretty well-crafted prompt. The whole app is available in this open-source GitHub repository. From the code I read, it looks like a frontend-only app, so how it handles the API key and its security is your responsibility.
You can read the FAQs on Google AI Studio Build/Apps page, which tell you that it is a frontend only app and other details about how it runs in an Iframe on Google Cloud Run.
The goal was to have a working app, and you have it, even with a dark and light theme switcher. It is a good starting point, but I would not consider it production-ready; use it cautiously and carefully. If you think something is wrong, delete the app from Cloud Run and/or delete the whole project. I don’t want you bleeding money on Google Cloud Platform.
Conclusion #
In this tutorial, you started with the goal of having a working Gen AI-powered and generated app that can guess the geolocation from a picture. You then generated the full app using Google AI Studio Apps/build feature. After that, you created and deployed a Google Cloud project to Google Cloud Run. Finally, you made changes to remove the OSINT mention from the user interface and redeployed the app to Google Cloud Run in the same Google Cloud Project.
It is pretty easy to go from an idea and prompt to a fully functional app accessible over the Internet and deployed on Google Cloud Run. To manage costs effectively, remember to monitor your Google Cloud billing and stop the app if needed. Keep learning and using Gemini and Google AI Studio!
