Google Cloud Shell Editor is like having a VS code editor inside of your browser that can be used to get most things done. In this post, you will use the Google Cloud Shell editor to pull in code from an open-source repository and deploy it to Cloud Run without leaving your browser. Let’s get started!

Table of contents #
- Google Cloud Shell Terminal
- Cloud Shell Editor
- Example code to pull in from GitHub
- Make a small change
- Deploy code to Cloud Run
- Check the working app
- Conclusion
Google Cloud Shell Terminal #
Google Cloud Shell is your online command center for Google Cloud. It's a pre-configured command line environment accessible directly from your web browser. You click an icon on the top right corner with a >_ sign, after you log in to your Google Cloud console to activate Cloud shell. After it is activated, it will open Cloud shell and you have access to a full-fledged interactive shell environment with bash, as seen below
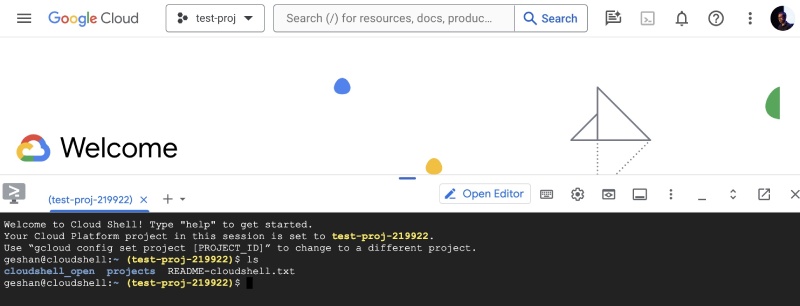
When it first appears, it is only half of the screen. You can pull it and expand it to be as long as you like. I have made it cover almost all of the browse space available.
You get a temporary Compute Engine Virtual machine that can be used for a maximum of 60 hours a week (official doc says 50 hours). It has gcloud command the Google Cloud SDK pre-installed and also has languages like Python, Java, Go and Node.js installed on it. You also get 5 GB of persistent storage. If you need a CLI tool, chances are it might already be there. If it is not there you can apt-get and get it but remember it is an ephemeral machine.
In addition to the shell terminal, you also get the Google Cloud Shell Editor which is a version of VS code inside the browser. That is discussed next with a code example which is deployed to Google Cloud Run.
Cloud Shell Editor #
Google Cloud Shell Editor is a web-based code editor that's included with every Cloud Shell instance. It lets you develop, build, debug, and deploy cloud-based applications directly from your browser, without needing to set up any local development environment. This online code editor has support the languages like JavaScript (Node.js), Java, Python and Go lang with features like syntax highlighting, code completion, linting, and debugging. You can access the Cloud Shell Code Editor by clicking the Open Editor button
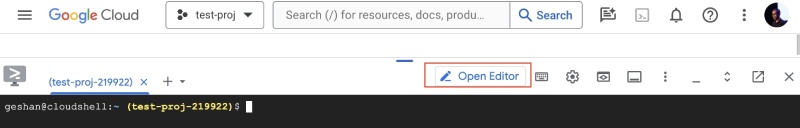
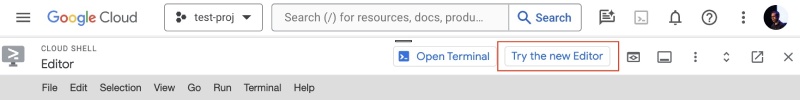
At first, you will get the legacy editor, to use the latest editor click the Try the new editor button, as seen below:
If all goes well, after you authorize and the machine is provisioned in some seconds (not minutes), you will see the Google Cloud Shell Editor as follows:
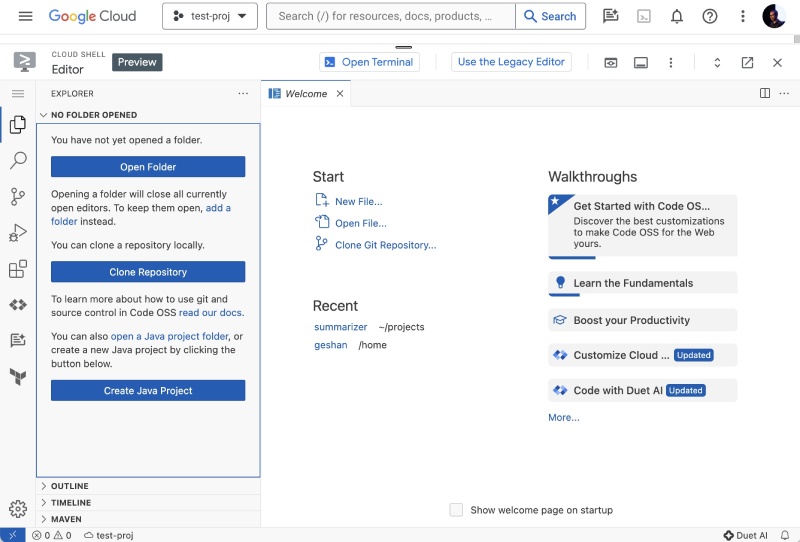
Hurray! You have a full-on VS-Code like editor inside your browser that great. In the next part, you will pull in a simple Node.js Express app and make some changes to it then deploy it to Google Cloud Run without leaving the browser window.
Example code to pull in from GitHub #
For this tutorial, you will use an example that creates a fictional landing page for a podcast called the “Eventually Podcast”. You can give your email address and Sign up to know when the podcast is launched, pretty simple. You can read about how it is made in this blog post about Next.js Express tutorial.
To pull in the code on your Google Cloud Shell machine VM you can run the following commands within the Google Cloud Shell Editor’s CLI editor. You can start a terminal window by clicking the hamburger menu then going to Terminal > New Terminal or hitting the relevant shortcut as per your operating system.
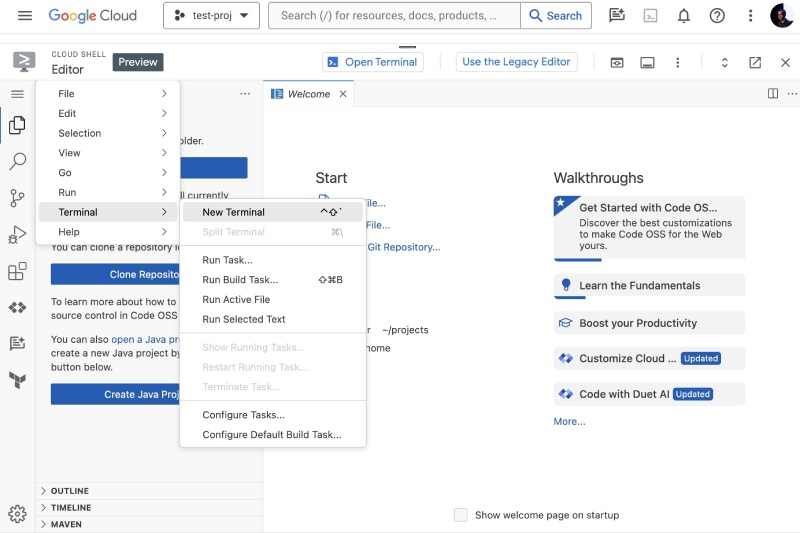
After that, you will see then the terminal inside your Google Cloud Shell environment as follows:
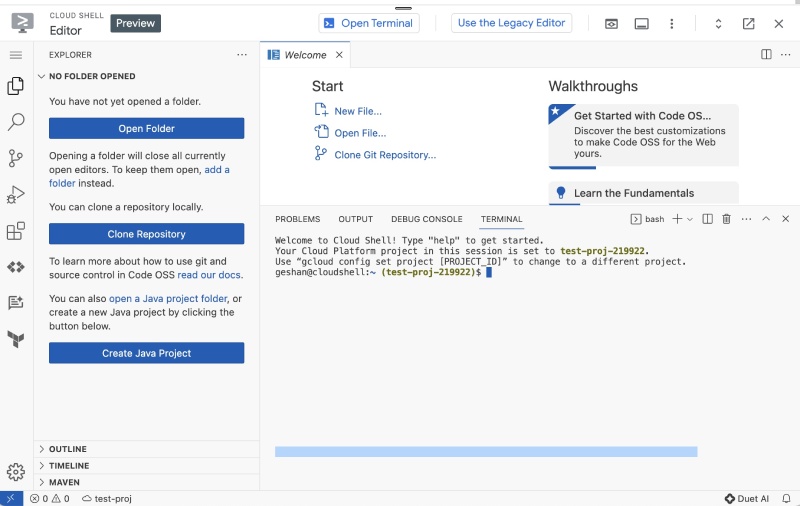
You can use the main terminal if you choose to but staying inside the editor and using this terminal is better. You can run the following commands to get the needed code from GitHub in the projects folder:
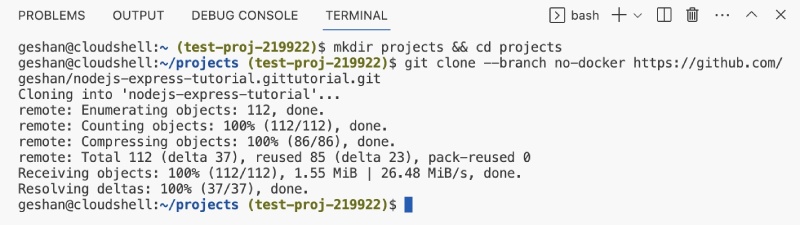
mkdir projects && cd projects
git clone --branch no-docker https://github.com/geshan/nodejs-express-tutorial.gitThe first line creates the projects folder and goes into it, the second line clones the repository needed for this example. There are a couple of things you should understand about the git clone. First is that it is cloning the no-docker branch, not the master branch and the second is it is using the https url not the [email protected]… URL to make things simple and jump the authentication hoop. When the commands are done it will look like the below:
Great! At this point, you have the code that you need in your Google Cloud Shell VM. Next, you will make a small change to get a feel of using the Google Cloud Shell Editor.
Make a small change #
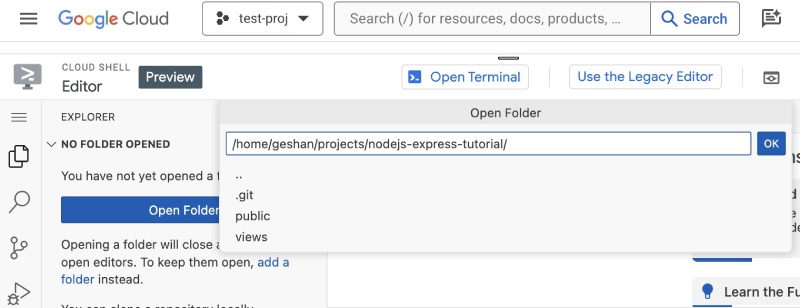
Given the needed code is on the virtual machine at ~/projects/nodejs-express-tutorial, it can be added to the code editor following the instructions below:
- Open
Explorer(if it is not open) - the first icon on the editor’s left bar - Then click
Open Folder - After that add
projectsto the path (which will be your home folder) - Then select
nodejs-express-tutorial - After that hit ok
That looks like the following:
It will take some time and the code will be loaded on the editor, open the index.js file as seen below:
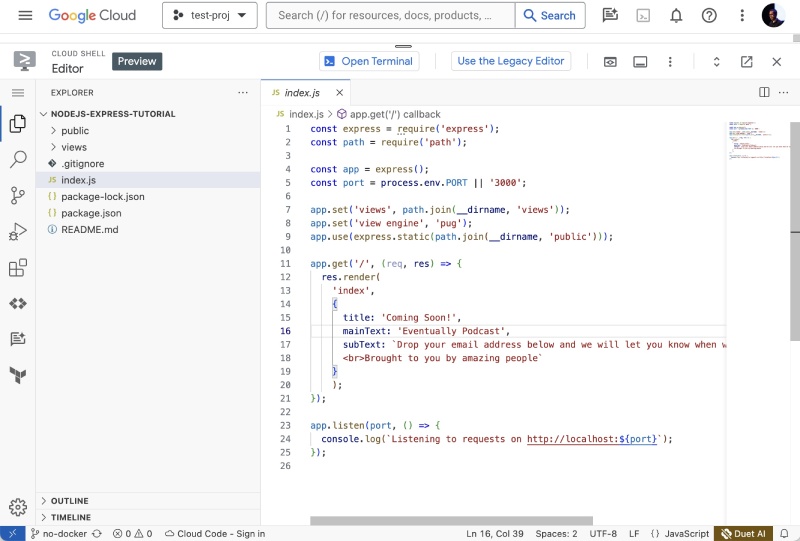
As you can see the syntax highlight is also there for the JavaScript file. Then add on Google Cloud Run. on the line no. 18 after amazing people as follows:
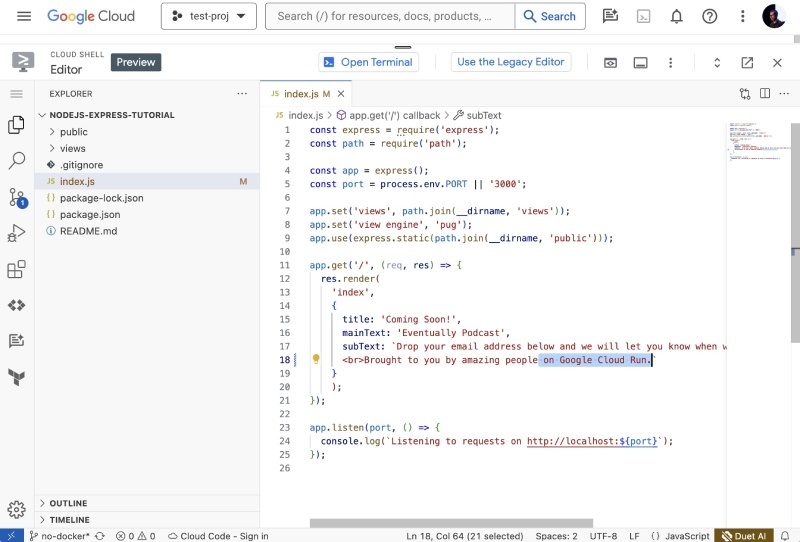
Now save the file, it is as easy as using an editor on your local machine. You can bring up the terminal again and see if the changes are reflected with a git status command which will show something like the below:
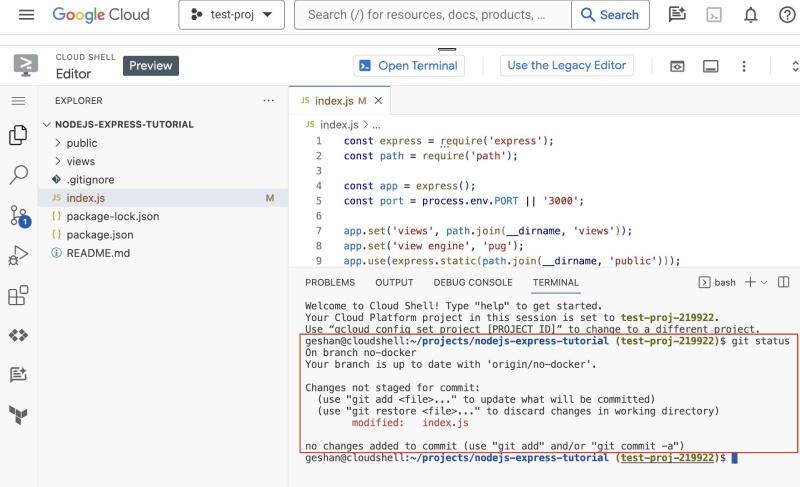
In the next section, you will deploy this code to Google Cloud Run.
Deploy code to Cloud Run #
As everything is integrated and authenticated. To deploy the code (even without dockerizing) you can run the following gcloud command and it will deploy the app to Google Cloud Run from the source. As this is a Node.js application which is one of the supported languages to be from source by Google Cloud Run, it will work even without having a Dockerfile.
gcloud run deploy eventually-podcast --source . --allow-unauthenticated --region=us-central1Here you are asking the service to be called eventually-podcast when deploying to Cloud Run from the source code available in the current folder . and make it accessible without any authentication. For this example, you chose us-central1 as the region, which can be changed depending on where you want to deploy the app. You can specify other parameters too like memory, cpu, and other. Read it in the official documentation of gcloud run deploy or ask Duet AI. When the command is executed from the nodejs-express-tutorial folder it will look like the below:
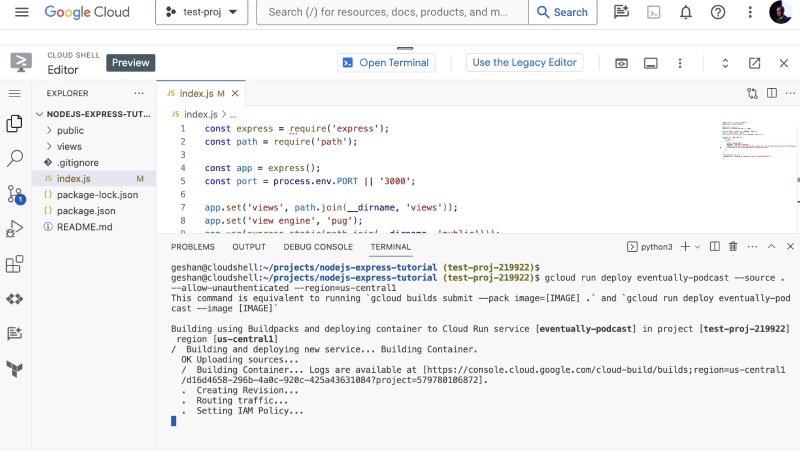
It will take some minutes to build the image from the source using buildpacks and then deploy it to Google Cloud Run. You might need to authorize some permissions if you are doing so for the first time. Many things happen in the background to get this job done. Once done it will look as follows:
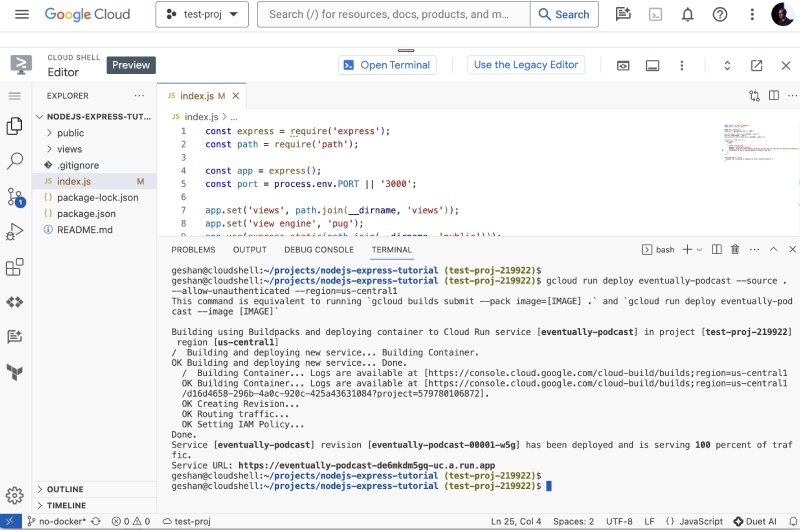
You will see a Cloud Run URL ending with .run.app where the app is running now.
Check the working app #
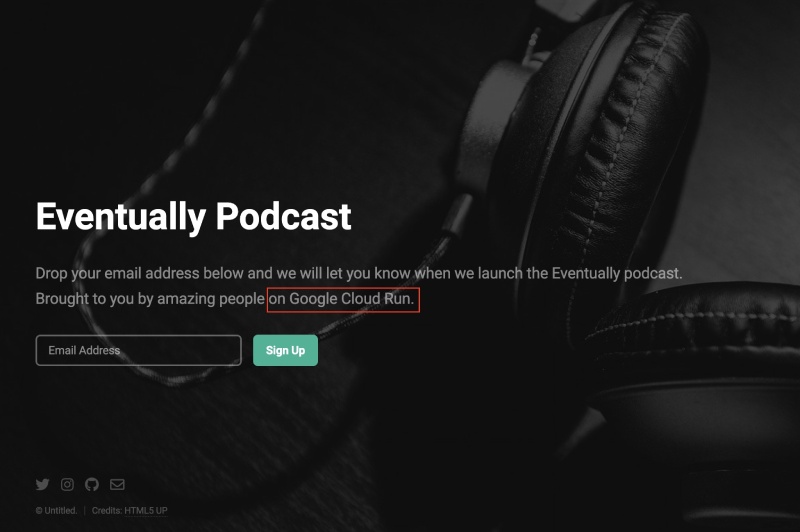
When you open the given URL on your browser you can see the app running on Google Cloud Run and also the change you made (highlighted in the screenshot below) as follows:
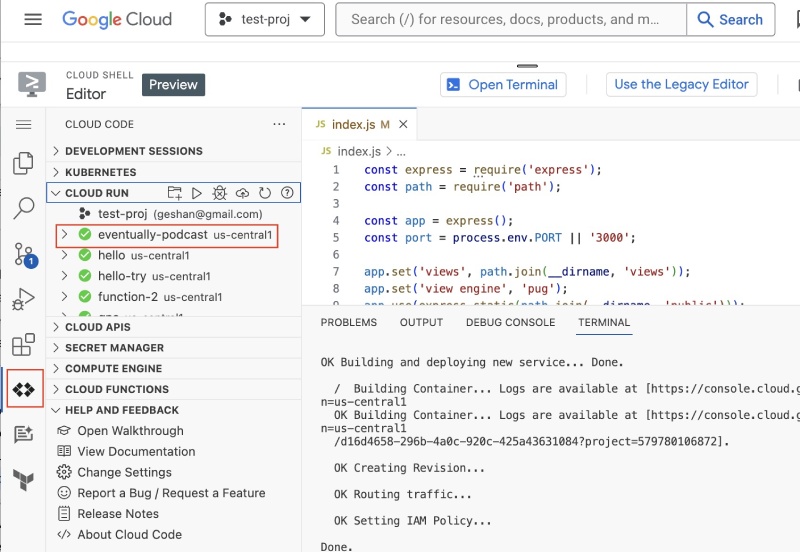
You can verify it by going to your Cloud Run services list page or by clicking the Cloud Code icon (the 6th icon on the left side) and then expanding Cloud Run in it as seen below:
There you have it, a step-by-step guide to getting code from any open-source GitHub repository (without generating any SSH key), then making a small change and deploying it to Google Cloud Run without leaving your browser.
As a side note:
Google Cloud Shell Editor can be one of the fastest and easiest ways to use and experience Google’s Duet AI for developers on a code editor.
That could be a good topic for another blog post. Anyhow, you can try some of your Gen AI and prompt engineering chops following this post on Node.js and Duet AI on VS Code.
Conclusion #
In this post, you were introduced to Google Cloud Shell Terminal and Google Cloud Shell Editor. Then you pulled code from a GitHub repository and used the Cloud Shell Editor to make a minor change. After that, you deployed it successfully to Google Cloud Run with a single command, without using Docker. Finally, you could see the app working with an HTTPS URL that ended in .run.app. As the app has unauthenticated access, it can be accessed by anyone in the world.
I hope you will utilize both the Cloud Shell terminal and Cloud Shell editor to your advantage and business benefits. Keep learning!
